https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1967
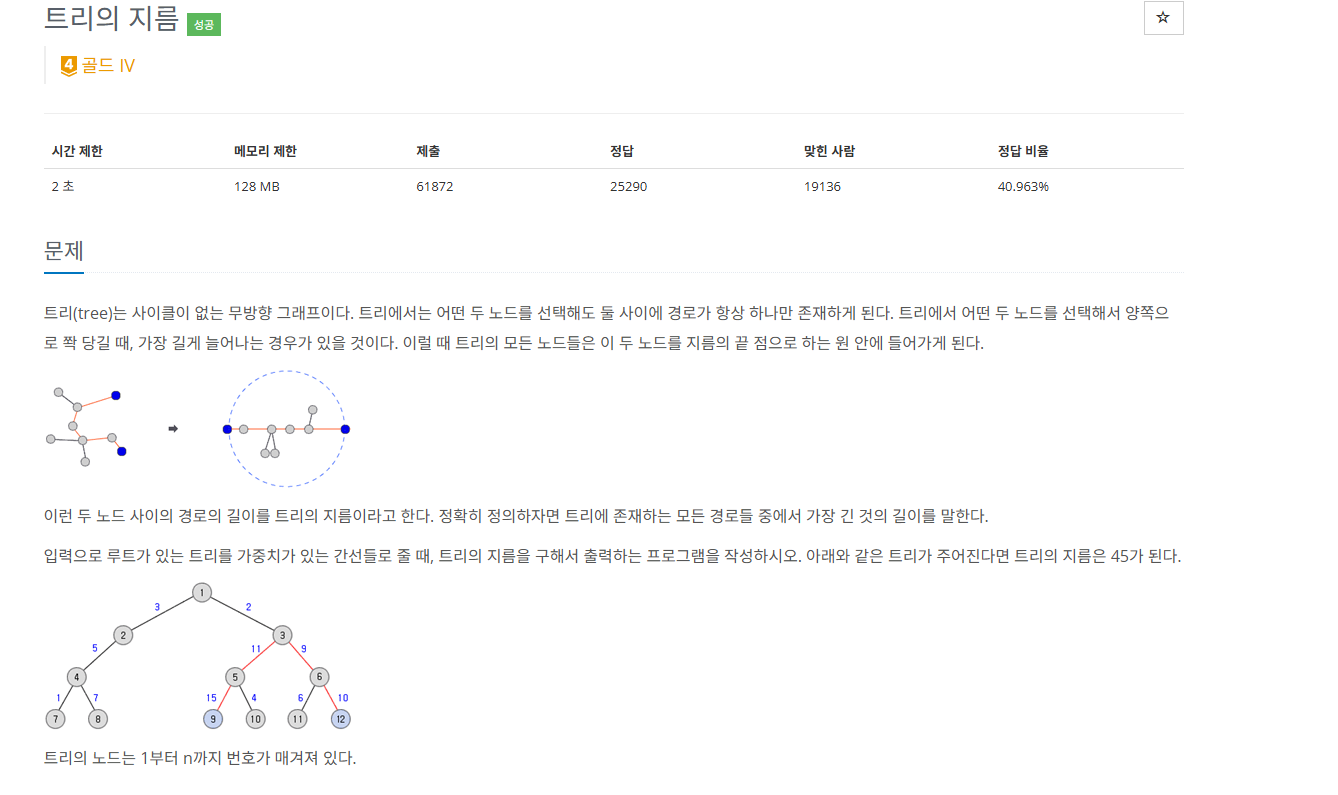
트리를 이루는 정점의 개수 N과 N-1개의 간선의 개수가 주어지면, 두 정점을 뽑아 일자로 만들 때 가장 긴 길이를 구하는 문제이다.
-> 정점 X와 정점 Y의 경로가 최장 경로일 때 경로의 길이
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int num = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
List<Point> nodeList = IntStream.range(0,num+1).mapToObj(Point::new).collect(Collectors.toList());
HashSet<Integer> fromSet = new HashSet<>();
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num-1; i++) {
int[] a = Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
nodeList.get(a[0]).add(new Line(a));
nodeList.get(a[1]).add(new Line(a[1],a[0],a[2]));
fromSet.add(a[0]);
sum+=a[2];
}
if(num<=3){
System.out.println(sum);
return;
}
if(fromSet.size()==1){
int targetNum = fromSet.iterator().next();
List<Line> temp = nodeList.get(targetNum).getList();
List<Integer> tempList = temp.stream().mapToInt(l -> l.weight).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList());
Collections.sort(tempList);
System.out.println(tempList.get(tempList.size()-1)+tempList.get(tempList.size()-2));
return;
}
boolean[] visited = new boolean[num+1];
bfs(nodeList,visited,1);
bfs(nodeList,visited,getMidx(nodeList));
System.out.println(getMax(nodeList));
}
static void bfs(List<Point> nodeList, boolean[] visited, int targetNum){
Queue<Line> q = new LinkedList<>();
nodeList.forEach(Point::init);
Arrays.fill(visited,false);
q.addAll(nodeList.get(targetNum).list);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Line l = q.poll();
int f = l.from;
int t = l.to;
int w = l.weight;
visited[f] = true;
Point p = nodeList.get(t);
p.weight = nodeList.get(f).weight+ w + p.weight;
for (Line line : nodeList.get(t).getList()) {
if(visited[line.to]) continue;
q.offer(line);
}
}
}
static int getMidx(List<Point> nodeList){
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int midx = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.size(); i++) {
if(max<nodeList.get(i).weight){
max = nodeList.get(i).weight;
midx = i;
}
}
return midx;
}static int getMax(List<Point> nodeList){
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int midx = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.size(); i++) {
if(max<nodeList.get(i).weight){
max = nodeList.get(i).weight;
midx = i;
}
}
return max;
}
}
class Point{
int value;
List<Line> list = new ArrayList<>();
int weight = 0;
Point(int v){
this.value = v;
}
List<Line> getList(){
return this.list;
}
void add(Line l){
list.add(l);
}
void init(){
this.weight = 0;
}
}
class Line{
int from;
int to;
int weight;
Line(int f, int t, int w){
this.from = f;
this.to = t;
this.weight = w;
}
Line(int[] a){
this.from = a[0];
this.to = a[1];
this.weight = a[2];
}
}
우선 임의의 정점 1개를 구해 BFS를 통해 각 정점까지의 거리를 구하고, 기준 정점에서 가장 먼 정점을 다시 기준으로 삼고, 해당 정점에서 가장 먼 정점을 구하면 그 정점까지의 거리가 최장거리이다.
이때 한 개의 정점만 여러개의 자식 노드를 가지는 경우와, 정점의 개수가 3개 이하일 경우를 각각 예외처리했는데, 첫번째 케이스는 모든 간선이 하나의 정점에서 비롯되었다면 그냥 간선 가중치를 기준으로 정렬해서 맨 뒤에 두 간선 가중치의 합을 반환해도 되기 때문이고 두번째 경우는 정점의 개수가 3개 이하라면 그냥 주어지는 가중치의 합을 반환하면 되기 때문이다.
'백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] 백준 5639 - 이진 검색 트리 (0) | 2025.08.22 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] 백준 1987 - 알파벳 (1) | 2025.08.19 |
| [JAVA] 백준 1753 - 최단경로 (4) | 2025.08.13 |
| [JAVA] 백준 1504 - 특정한 최단경로 (2) | 2025.08.12 |
| [JAVA] 백준 1043 - 거짓말 (2) | 2025.08.12 |

